At the International Conference on Creationism 2013 (ICC 2013), professional geneticist Jeffrey Tomkins (along with Jerry Bergman) delivered a devastating critique of the claim that humans are 98% genetically similar to chimps. What he demonstrated was the fact that Darwinists are essentially saying “what is similar is 98% similar”, which is cherry picking. Tomkins acknowledges we are closer to chimps than daffodils, but humans are still substantially different from chimps.
I posted a less technical complaint here: With no dictionary tricks, humans only 70% similar to chimps.
Recall the “dictionary trick” whereby Tom Wolfe’s famous novel The Right Stuff can be shown to be almost 100% identical to a dictionary merely by aligning the words in Wolfe’s novel against identical words in the dictionary. The illusion of similarity is brought about by a total disregard for sentence structure and context of the words within sentences, paragraphs, and chapters. When those considerations are taken into account, it becomes preposterous to assert The Right Stuff is almost 100% identical to a dictionary. But such illegitimate lines of comparison are the staple of evolutionism.
Tomkins described the origin of the fallacious comparison as a myth that got started in reassociation kinetic methods of comparison in the mid-1970’s prior to the advent of modern sequencing techniques (like Illumina and Solexa). Reassociation kinetics was a technique where fragments of chimp and human DNA were mixed in the same chemical soup, and the DNAs that were reasonably similar would pair up, hence we got a biased sampling!
If we take genes that are found in both humans and chimps and disregard the indels, we get the 98% figure. When indels are considered, the similarity drops to 80-85%!
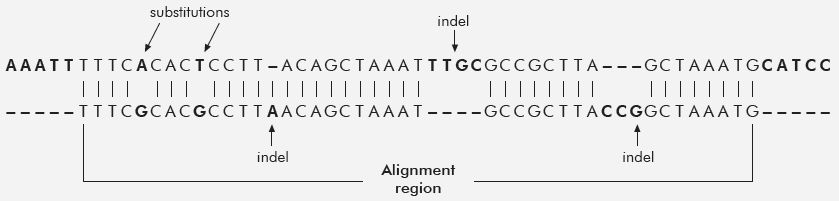
When including other sequences, the similarity drops even further, down to 70%. But that 70% figure itself, imho, is too generous. I don’t think Tomkins used ORFans or pseudo genes or many other intergenic sequences, and he explicitly avoided the complication of Synteny. The links below go into detail. One might argue, the indels don’t have function. We don’t know that as a general rule, and even if they didn’t it still is a problem for evolution to account for how the indels got fixed into a population.
Tomkins pointed also to reports where lab workers may have contaminated the sequencing labs for Chimps with their own human DNA and thus biasing the figures! Hence re-sequencing has been done, and there is more sequencing pending to clean up these errors. He joked about the coughing and sneezing that may have gone on to cause contamination.
Further he pointed out that it seemed politically incorrect to dispute the 98% figure promoted by the reassociation kinetics work because it accorded with the false evolutionary narrative. He said, the industry is finally having to “fess up”, that some of their conclusions are “bogus”.
Tomkins has been reviewer on peer reviewed papers on genetics, he ran a genome lab at Clemson, and said if he had been the reviewer of some of the evolutionary papers he would have rejected them for publication because of the lack of clarity in their methodology, particularly in the material and methods sections of the paper.
During the answer and question session, a ranting raving evolutionary biologists gets up and whines and says something to the effect, “you’re using such inflammatory language … ‘sneeze and cough and ‘fess up’ and bogus'”. The evolutionary biologist then said, “as I said, what I have problems with is inflammatory your language, I don’t want to get into the technical details.” When he said that, he got laughed off stage. It was obvious Tomkins made an unassailable case and the evolutionary biologist didn’t want to be engage Tomkins technical assertions. Instead the evolutionary biologist grasped at irrelevant straws like Tomkins use of the words “sneeze” and “cough”. Pathetic!
Along those lines, I’ll give a sample of inflammatory language:
In science’s pecking order, evolutionary biology lurks somewhere near the bottom, far closer to phrenology than to physics
Jerry Coyne
Oh wait, that’s an evolutionist making inflammatory remarks about his own discipline, not a creationist.
I told Jeff, “I accepted the 98% figure for years, I thought it was true, creationists since Linnaeus have said we’re more similar to apes than to trees.” Jeff replied something to the effect, “that’s a good point, I accepted the 98% figure too, and I was prepared to accept it if that’s what my research indicated.” Tomkins spent 3 months reviewing the NCBI sequences himself, and Bergman devoted time to assist going through the literature. This was no small project. Tomkins lists recent peer-reviewed literature that supports his points.
Chimp/human similarity wasn’t directly a question of creation and evolution, it is a basic empirical question of the similarity in evidence today. If evolutionary biologists can’t be forthright and accurate about even basic empirical questions of data in the present day, why should they be trusted with speculations about the deep past?
NOTES:
Jeffrey Tomkins, Ph.D. (Genetics)
Jeffrey Tomkins has a Ph.D. in Genetics from Clemson University, a M.S. in Plant Science from the University of Idaho, Moscow and a B.S. in Agriculture from Washington State University. He was on the Faculty in the Dept of Genetics and Biochemistry, Clemson University, for a decade where he worked as a research technician in a plant breeding/genetics program, focusing on quantitative and physiological genetics in soybean. He is now a Staff Scientist at ICR. He has 56 publications in peer reviewed scientific journals and seven book chapters in scientific books. He is the primary author of The Design and Complexity of the Cell.
http://creation.com/dr-jeffrey-tomkins
Articles
The chromosome 2 fusion model of human evolution—part 1: re-evaluating the evidence
The chromosome 2 fusion model of human evolution—part 2: re-analysis of the genomic data
The junk DNA myth takes a well-deserved hit
Genomic monkey business—estimates of nearly identical human–chimp DNA similarity re-evaluated using omitted data
Is the human genome nearly identical to chimpanzee?—a reassessment of the literature
PS
Jerry Bergman had been an atheist while a professor before he got expelled. Thankfully he got rehired at a medical college where he has been teaching for the last 27 years.
Jerry Bergman, Ph.D., Biology
Biography
Jerry Bergman has taught biology, genetics, chemistry, biochemistry, anthropology, geology, and microbiology at Northwest State College in Archbold OH for over 25 years. He has 9 degrees, including 7 graduate (= ‘post-graduate’ in some non-US systems) degrees. Dr Bergman is a graduate of Medical College of Ohio, Wayne State University in Detroit, The University of Toledo, and Bowling Green State University. He has over 800 publications in 12 languages and 20 books and monographs. He has also taught at the Medical College of Ohio where he was a research associate in the department of experimental pathology, and he also taught 6 years at the University of Toledo, and 7 years at Bowing Green State University.
Among his books is a monograph on peer evaluation published by the College Student Journal Press, a Fastback on the creation-evolution controversy published by Phi Delta Kappa, a book on vestigial organs with Dr George Howe (‘Vestigial Organs’ are Fully Functional), a book on psychology and religious cults, a book on religious discrimination published by Onesimus Press, and a book on mental health published by Claudius Verlag in München. He has also published a college textbook on evaluation (Boston, Houghton Mifflin Co.), and has contributed to dozens of other textbooks. He was also a consultant for over 20 science text books, mostly biology and biochemistry.
Dr Bergman has presented over one hundred scientific papers at professional and community meetings in the United States, Canada, and Europe. To discuss his research, he has been a featured speaker on many college campuses throughout the United States and Europe, and is a frequent guest on radio and television programs. His research has made the front page in newspapers throughout the country, has been featured by the Paul Harvey Show several times, and has been discussed by David Brinkley, Chuck Colson, and other nationally known commentators on national television.
His other work experience includes over ten years experience at various Mental Health/Psychology clinics as a licensed professional clinical counselor and three years full time corrections research for a large county circuit court in Michigan and inside the walls of Jackson Prison (SPSM), the largest walled prison in the world. He has also served as a consultant for CBS News, ABC News, Reader’s Digest, Amnesty International, several government agencies and for two Nobel Prize winners, including the inventor of the transistor. In the past decade he has consulted or has testified as an expert witness or consultant in almost one-hundred court cases. A Fellow of the American Scientific Association, member of The National Association for the Advancement of Science, and many other professional associations, he is listed in Who’s Who in America, Who’s Who in the Midwest and in Who’s Who in Science and Religion.
Education
M.P.H., Northwest Ohio Consortium for Public Health (Medical College of Ohio, Toledo, Ohio; University of Toledo, Toledo, Ohio; Bowling Green State University, Bowling Green, Ohio), 2001.
M.S. in biomedical science, Medical College of Ohio, Toledo, Ohio, 1999.
Ph.D. in human biology, Columbia Pacific University, San Rafael, California, 1992.
M.A. in social psychology, Bowling Green State University, Bowling Green, Ohio, 1986.
Ph.D. in measurement and evaluation, minor in psychology, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan, 1976.
M.Ed. in counseling and psychology, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan, 1971.
B.S., Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan, 1970. Major area of study was sociology, biology, and psychology.
A.A. in Biology and Behavioral Science, Oakland Community College, Bloomfield Hills, Michigan, 1967.
http://creation.com/dr-jerry-bergman