 |
Reading through a recent article by KeithS over at The Skeptical Zone, I was reminded of the following lyrics from the musical Annie Get Your Gun:
Anything you can do,
I can do better.
I can do anything
Better than you.No, you can’t.
Yes, I can. No, you can’t.
Yes, I can. No, you can’t.
Yes, I can,
Yes, I can!
The article, which is entitled, Things That IDers Don’t Understand, Part 1 — Intelligent Design is not compatible with the evidence for common descent, argues that evolution guided by an Intelligent Designer fares much worse – in fact, trillions of times worse – than unguided Darwinian evolution as an explanation of how living things arose in all their diversity, because whereas Darwinian evolution is the only way in which unguided natural processes could have generated the life-forms we see on Earth today, the probability of an Intelligent Designer choosing to make living things in a way that mimics unguided Darwinian evolution is very, very low: there were so many other ways in which the Designer might choose to produce life on Earth rather than by mimicking such a process.
KeithS’s article discusses a very striking feature exhibited by living things: the fact that they fall into “groups within groups”, or what biologists refer to as a nested hierarchy. EvoWiki provides a useful definition of this term:
“Nested hierarchy” refers to the way taxonomic groups fit neatly and completely inside other taxonomic groups. For instance, all bats (order Chiroptera) are mammals. All mammals are vertebrates. Likewise, all whales (order Cetacea) are also mammals, and thus also vertebrates.
While it might seem that this arrangement is obvious and unavoidable, it is not. Taxonomic groups are defined by traits and it should be possible to mix traits from multiple defined groups. An example from classical mythology is the Pegasus, a creature with features defined as both mammal (produces milk like a horse) and bird (has feathers). Mammals and birds are both orders, so, if Pegasus existed, it would be a violation of the nested hierarchy, a creature that belonged to two separate groups. Likewise for satyrs (human torso, goats legs), jackalopes (rabbit body with an antelope head) and crocoducks (crocodile head, body of a duck)…
Life, however, shows a clear nested hierarchy, at least with regards to multicellular organisms. An animal that produces milk (Mammals), will also have hair, have four limbs, be endothermic (warmblooded) plus possess many other characteristics. Why should this be? Why do no other animals or plants produce milk? Why do no mammals have four limbs plus a pair of wings, like the Pegasus or angels?
Hierarchies are a very common feature of the world in which we live. However, not all hierarchies are nested hierarchies. Nested hierarchies involve levels which consist of, and contain, lower levels. For example, an army consists of a collection of soldiers and is made up of them. Thus an army is a nested hierarchy. Non-nested hierarchies, on the other hand, are more general, in that they relax the requirement that higher levels should contain the levels below them. For instance, the general at the top of a military command does not consist of his soldiers: they are distinct from him, and he doesn’t “contain” them. Thus the military command (unlike the army) is a non-nested hierarchy, with regard to the soldiers in the army. In general, all pecking orders are non-nested hierarchies. And in the natural world, food chains are excellent examples of non-nested hierarchies.
Dr. Douglas Theobald explains why the nested hierarchy we find in living things is such a powerful piece of evidence for Darwinian evolution in his article, 29+ Evidences for Macroevolution: The Scientific Case for Common Descent (Prediction 1.2: A nested hierarchy of species):
As seen from the phylogeny in Figure 1, the predicted pattern of organisms at any given point in time can be described as “groups within groups”, otherwise known as a nested hierarchy. The only known processes that specifically generate unique, nested, hierarchical patterns are branching evolutionary processes. Common descent is a genetic process in which the state of the present generation/individual is dependent only upon genetic changes that have occurred since the most recent ancestral population/individual. Therefore, gradual evolution from common ancestors must conform to the mathematics of Markov processes and Markov chains. Using Markovian mathematics, it can be rigorously proven that branching Markovian replicating systems produce nested hierarchies (Givnish and Sytsma 1997; Harris 1989; Norris 1997). For these reasons, biologists routinely use branching Markov chains to effectively model evolutionary processes, including complex genetic processes, the temporal distributions of surnames in populations (Galton and Watson 1874), and the behavior of pathogens in epidemics…
…[I]f common descent is true, then in some time frame we will always be able to observe a nested hierarchy for any given character. Furthermore, we know empirically that different characters evolve at different rates (e.g. some genes have higher background mutation rates than others). Thus, if common descent is true, we should observe nested hierarchies over a broad range of time at various biological levels. Therefore, since common descent is a genealogical process, common descent should produce organisms that can be organized into objective nested hierarchies.
For anyone who may be wondering what a Markov process is, Wikipedia provides an easily accessible definition:
A Markov chain (discrete-time Markov chain or DTMC) named after Andrey Markov, is a mathematical system that undergoes transitions from one state to another, between a finite or countable number of possible states. It is a random process usually characterized as memoryless: the next state depends only on the current state and not on the sequence of events that preceded it. This specific kind of “memorylessness” is called the Markov property.
I’d now like to discuss the recent article by KeithS, over at The Skeptical Zone. His key point is a very simple one. What Darwinian evolution explains spectacularly well about life is the striking fact that organisms can be grouped into objective nested hierarchies. As we saw above, gradual evolution from common ancestors must conform to the mathematics of Markov processes and Markov chains, which automatically generate nested hierarchies in replicating systems that branch. The process of Intelligent Design, on the other hand, need not generate organisms that can be grouped into objective nested hierarchies: all we can say is that it might.
A puzzle about an apartment dweller
 |
Marina City in Chicago, Illinois, United States, which was built in 1959, was a landmark in apartment construction. Image courtesy of Wikipedia.
In order to properly appreciate the point that KeithS makes in his article, let’s consider the following puzzle (which some readers will have encountered before) about an apartment dweller with a rather strange habit:
A man lives on the 26th floor of an apartment building. He takes the elevator every day, when he goes to work. When he comes back from work, he doesn’t take the elevator up to the 26th floor, where he lives. Instead, he takes the elevator up to the 12th floor. Why does he do this?
When I put this puzzle to people who haven’t heard it before, most of them come up with an ad hoc rationalization: “Maybe he needs the exercise,” “Maybe the elevator is very crowded in the evening, so he gets out half-way up because he needs to get some fresh air,” or “Maybe he has a girlfriend who lives on the 12th floor.” These are perfectly fine explanations of why the man might get off at the 12th floor, but they all share a common failing: they fail to explain why he must get off at that floor. There’s only explanation that can account for this singular fact, and as soon as we hear it, we instantly recognize that it must be the right explanation: the man is a dwarf, and he can’t reach the button for the 26th floor.
What KeithS is arguing, then, is that Darwinian evolution is the true explanation for the striking fact that living things fall into “groups within groups” (or what we call a nested hierarchy) because it’s the only account that tells us why they must exhibit this property, whereas Intelligent Design explanations of this fact are merely ad hoc rationalizations which at best, can only tell us why living things may fall into a nested hierarchy. Thus Darwinian evolution wins “hands down”, as an explanation of the nested hierarchy into which living things can be classified.
KeithS: Why Darwinian evolution is a much better explanation of the nested hierarchy into which living things can be classified than intelligently guided evolution
It might seem as if the foregoing argument would only work against Intelligent Design proponents who reject common descent and who hold that each kind of organism was created separately. But KeithS contends that even Intelligent Design advocates like myself, who accept the evidence for common descent, are unable to provide a good explanation for the nested hierarchy we find in living things. The problem is that whereas Darwinian evolution automatically generates this nested hierarchy, guided evolution does not, which means that people who support guided evolution have to fall back on the lame, ad hoc explanation that “the Designer just wanted it that way”:
In other words, our ‘common descent IDers’ face a dilemma like the one faced by the creationists. They can force guided evolution to match the evidence, but only by making a completely arbitrary assumption about the behavior of the Designer. They must stipulate, for no particular reason, that the Designer restricts himself to a tiny subset of the available options, and that this subset just happens to be the subset that creates a recoverable, objective, nested hierarchy of the kind that is predicted by unguided evolution. Unguided evolution doesn’t require any such arbitrary assumptions. It matches the evidence without them, and is therefore a superior explanation. And because unguided evolution predicts a nested hierarchy of the kind we actually observe in nature, out of the trillions of alternatives available to a Designer who guides evolution, it is literally trillions of times better than ID at explaining the evidence.
In a nutshell: KeithS contends that a Design-based explanation of the nested hierarchy into which living things can be classified is inferior to a naturalistic one, because it doesn’t specifically generate a nested hierarchy, whereas an unguided, naturalistic evolutionary process does. As Dr. Douglas Theobald puts it: “The only known processes that specifically generate unique, nested, hierarchical patterns are branching evolutionary processes” (italics mine).
And because the nested hierarchy into which living things can be classified isn’t just an “incidental” feature of living things, but an all-pervasive, defining feature that applies to all kinds of organisms, we can confidently say that Darwinism is a much better explanation of life in general than Intelligent Design.
Case closed, right? Not so fast.
Why cars don’t work as a counter to KeithS’s argument
 |
A photograph of the original Benz Patent-Motorwagen, first built in 1885 and awarded the patent for the concept. Image courtesy of Wikipedia.
Before I put forward an Intelligent Design explanation of the nested hierarchy that all species of living things belong to, I’d like to discuss a bad explanation for the nested hierarchy which in my opinion simply doesn’t work.
Dr. Theobald, author of 29+ Evidences for Macroevolution: The Scientific Case for Common Descent, is well aware of the common creationist counter-argument that some designed artifacts, such as cars, also exhibit a nested hierarchy like the one we find in Nature. Actually, he says, most artifacts don’t exhibit an objective hierarchy, in the way that living things do:
Although it is trivial to classify anything subjectively in a hierarchical manner, only certain things can be classified objectively in a consistent, unique nested hierarchy. The difference drawn here between “subjective” and “objective” is crucial and requires some elaboration, and it is best illustrated by example. Different models of cars certainly could be classified hierarchically — perhaps one could classify cars first by color, then within each color by number of wheels, then within each wheel number by manufacturer, etc. However, another individual may classify the same cars first by manufacturer, then by size, then by year, then by color, etc. The particular classification scheme chosen for the cars is subjective.
… Which types of car characters are more important depends upon the
personal preference of the individual who is performing the classification. In other words, certain types of characters must be weighted subjectively in order to classify cars in nested hierarchies; cars do not fall into natural, unique, objective nested hierarchies.
Dr. Theobald goes on to say that inanimate objects typically don’t fall into nested hierarchies, whereas living organisms do:
Interestingly, Linnaeus, who originally discovered the objective hierarchical classification of living organisms, also tried to classify rocks and minerals hierarchically. However, his classification for non-living objects eventually failed, as it was found to be very subjective. Hierarchical classifications for inanimate objects don’t work for the very reason that unlike organisms, rocks and minerals do not evolve by descent with modification from common ancestors.
The degree to which a given phylogeny displays a unique, well-supported, objective nested hierarchy can be rigorously quantified. Several different statistical tests have been developed for determining whether a phylogeny has a subjective or objective nested hierarchy, or whether a given nested hierarchy could have been generated by a chance process instead of a genealogical process (Swofford 1996, p. 504). These tests measure the degree of “cladistic hierarchical structure” (also known as the “phylogenetic signal”) in a phylogeny, and phylogenies based upon true genealogical processes give high values of hierarchical structure, whereas subjective phylogenies that have only apparent hierarchical structure (like a phylogeny of cars, for example) give low values (Archie 1989; Faith and Cranston 1991; Farris 1989; Felsenstein 1985; Hillis 1991; Hillis and Huelsenbeck 1992; Huelsenbeck et al. 2001; Klassen et al. 1991).
A nested hierarchy is a necessary property of individual organisms and of ecosystems
Dr. Theobald’s reply is a telling one. But before we continue, let’s ask ourselves this question: why don’t cars and other inanimate objects exhibit an objective nested hierarchy? Dr. Theobald thinks it’s because they’re not related by common descent, as living things are: the first car didn’t “beget” its successors, such as the Model T or the Ford Mustang. I disagree: I think it’s because they’re not alive. What I’m going to propose is that the nested hierarchical taxonomy into which the various kinds of organisms can be classified, and the nested hierarchical structure of an ecosystem, which is composed of populations of organisms, each of which is composed of organs, tissues and cells, are really two sides of one and the same coin. I would also contend that nested hierarchy of structure is an essential property of organisms, but not of artifacts such as cars.
In an article entitled, “Hierarchy: Perspectives for ecological complexity” (The Philosophy of Ecology: From Science to Synthesis edited by David R. Keller and Frank Benjamin Golley, University of Georgia Press, 2000), authors T. F. H. Allen and Thomas B. Starr describe two nested hierarchies that pervade the entire field of biology: the taxonomic hierarchy, which reflects the way in which each and every kind of living thing can be scientifically classified (a species belongs to a genus, which belongs to a family, which belongs to an order, which belongs to a class, which belongs to a phylum, which belongs to a kingdom, which belongs to a domain), and the structural hierarchy that we find not only within the body of each individual organism (which is made of up of organ systems, which are made up of organs, which are made up of tissues, which are made up of cells), but also within the larger community to which it belongs: an individual is a member of a population of organisms, which belongs to an ecosystem:
The notion of hierarchical arrangement is central to biology and even has an Aristotelian origin. The two standard ways of organizing biological systems, that is, into taxonomic units and structural relationships, both represent nested hierarchies. A nested hierarchy is one where the holon at the apex of the hierarchy contains and is composed of all lower holons. [A holon is something that is both a whole and a part. You are a whole, as an individual. You are also a part of society: no man is an island. – VJT] The apical holon consists of the sum of the substance and the interactions of all its daughter holons, and is, in that sense, derivable from them. Individuals are nested within populations, organs within organisms, tissues within organs, and tissues are composed of cells. In taxonomy a family consists of its constituent genera and their component species. These two hierarchical arrangements are ubiquitous in modern biology to such an extent that these arrangements are commonly used to order the material in introductory textbooks. (p. 228)
The authors go on to point out that there are also many non-nested ecological structures. But the point I’d like to make here is that the taxonomic hierarchy described by Dr. Theobald 29+ Evidences for Macroevolution: The Scientific Case for Common Descent and discussed by KeithS in his recent post isn’t the only nested hierarchy in the field of biology: it exists alongside a structural hierarchy that we also find in Nature. Dr. Lukas Buehler, in his life science forum “What is Life?”, provides an excellent summary of this nested structural hierarchy on a Web page entitled, Life can be studied as a hierarchical structure.
Now, it is easy for most laypeople to recognize that the body of a multicellular organism is a nested hierarchy with multiple levels, being made up of organ systems, which are made up of organs, which are made up of tissues, which are made up of cells. What is not so commonly appreciated, however, is the fact that the ecosystems to which these organisms belong are also nested hierarchies. This can be readily verified if one examines the various definitions of the term Ecosystem that can be found in the Environmental Benefits Analysis (EBA) program glossary published by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Among the definitions listed are the following:
Definition: a spatially and functionally nested hierarchy of air, land, and water units that include all the biotic and abiotic components within its boundaries.
Source: EBA Workgroup Manuscript : Smith et al and (Forman and Godron 1986, SERI 2004). The Role of Reference in Ecosystem Restoration.
Definition: a biotic community, together with its physical environment, considered as an integrated unit. Implied within this definition is the concept of a structural and functional whole, unified through life processes. Ecosystems are hierarchical, and can be viewed as nested sets of open systems in which physical, chemical and biological processes form interactive subsystems. Some ecosystems are microscopic, and the largest comprises the biosphere. Ecosystem restoration can be directed at different-sized ecosystems within the nested set, and many encompass multi-states, more localized watersheds or a smaller complex of aquatic habitat.
Source: HEAT Manual – Burks-Copes et al. 2008
Definition: A biotic community, together with its physical environment, considered as an integrated unit. Implied within this definition is the concept of a structural and functional whole, unified through life processes. Ecosystems are hierarchical, and can be viewed as nested sets of open systems in which physical, chemical and biological processes form interactive subsystems. Some ecosystems are microscopic, and the largest comprises the biosphere. Ecosystem restoration can be directed at different-sized ecosystems within the nested set, and many encompass multi-states, more localized watersheds or a smaller complex of aquatic habitat.
Source: MRGBER Feasibility Study Habitat Assessment : Analyses, Results and Documentation (Burks-Copes et al.)
Definition: An ecosystem is the dynamic and interrelating complex of plant and animal communities and their associated nonliving environment, considered as an integrated unit. Implied within this definition is the concept of structure and function unified through life processes. An ecosystem may be characterized as a viable unit of community and interactive habitat. Ecosystem restoration can be directed at different sized ecosystems within the nested set, and may encompass multiple states, more localized watersheds, or a smaller complex of aquatic habitats.
Source: Planning and Guidance Notebook, Engineer Regulation 1105-2-100, 22 April 2000
http://140.194.76.129/publications/eng-regs/er1105-2-101/toc.htm
In short: living things embody, in their very anatomy, a nested hierarchy of ends. What’s more, a nested hierarchy is also an inherent feature of the ecosystems to which individual organisms belong. But why would this structural hierarchy of life go hand in hand with a corresponding taxonomic hierarchy?
In order to answer this question, we first need to understand a fundamental property of living organisms: their dedicated functionality. The entire functional repertoire of each part of a living thing is “dedicated” to supporting the functionality of the organism it belongs to. (Note: By “the entire repertoire” of a part, I mean everything that it currently does. The parts of a living thing may have other potential uses: genes and even organelles can be exchanged between organisms, as shown by the phenomena of lateral gene transfer and endosymbiosis, respectively.)
Dr James Tour, the T. T. and W. F. Chao professor of chemistry and computer science at Rice University, explains the concept of embedded functionality using the illustration of a tree:
Dr. Tour explains: “[Let’s say that] you see a tree [and] you want to make a table, [so] you chop down the tree [and] you make a table – that’s [building] top down. But, the tree and I and everything else in nature are built from the bottom up. Molecules have certain embedded interactions between them and embedded functionality. Those come together to form higher-order structures called cells and those form higher-order structures and here we are.” You might also envision this as building from the inside out, or by forming the required traits in the smallest conceivable building blocks first.
(Interview with D. Geer: “Organic Computing: Life that Computes”, in TechWorthy.com magazine, Bedford Communications, 2002.)
I might mention in passing that this method of building living things is precisely the opposite of the way in which many critics of Intelligent Design (both religious and non-religious) imagine that God would produce living things. For instance, in a comment on a post entitled, Nature versus Art (April 30, 2011), Professor Feser asserted that God could, if He wished, make a man from the dust of the ground, simply by saying, “Dust, become a man.” When I asked him about the sequence of steps involved in such a transformation, he wrote back:
Forming a man from the dust of the ground involves causing the prime matter which had the substantial form of dust to take on instead the substantial form of a man. I’m not sure what “sequence of steps” you have in mind. There’s no sequence involved (nor any super-engineering – God is above such trivia). It’s just God “saying,” as it were: “Dust, become a man.” And boom, you’ve got your man.
… We have to work through other pre-existing material substances and thus have to do engineering and the like in order to make things. God, who is immaterial, the source of all causal power, etc. doesn’t need to do that and indeed cannot intelligibly be said to do it.
As I see it, the problem with merely telling the dust to become a man is that it under-specifies the effect – or in philosophical jargon, under-determines it. (What kind of man is the dust supposed to become? A tall one or a short one? Brown eyes or blue? A Will Smith lookalike or a Tom Cruise replica? Blood type A, B, AB or O? Exactly how many cells should this individual have? What sequence of bases should he have in his DNA?) And since dust, by itself, is unable to make a choice between alternatives – even a random one – then nothing at all will get done, if God commands dust to simply become a man. In order for God to generate a real man, every single detail in the man’s anatomy has to be specified, right down to the atomic level, and not even a Deity can make a man without specifying these details.
In short: making a living thing properly requires making it with a nested hierarchy of organization, in which its components and sub-components are specified in detail, right down to the level of the cell and its constituent molecules. But this is a structural nested hierarchy. What we still need to explain is why living things also exhibit a taxonomic hierarchy.
The programming of life
Professor Daniel Koshland Jr. (1920-2007), who was the editor of the leading US science journal, Science, from 1985 to 1995, listed seven essential properties of living things in a widely cited article entitled, The Seven Pillars of Life. The first of these properties is a program:
The first pillar of life is a Program. By program I mean an organized plan that describes both the ingredients themselves and the kinetics of the interactions among ingredients as the living system persists through time. For the living systems we observe on Earth, this program is implemented by the DNA that encodes the genes of Earth’s organisms and that is replicated from generation to generation, with small changes but always with the overall plan intact. The genes in turn encode for chemicals — the proteins, nucleic acids, etc. — that carry out the reactions in living systems. It is in the DNA that the program is summarized and maintained for life on Earth.
I should point out that Darwinian biologists do not envisage the genetic program we find in each organism as a product of design. That is because they typically envisage design in purely top-down terms, along the lines of a blueprint, and a genetic program isn’t like that, as Professor Richard Dawkins points out in his best-selling book, The Greatest Show on Earth (Transworld Publishers, London, Black Swan edition, 2010. There is a significant difference between a blueprint and an embryo’s developmental program: a blueprint is a planned form of architecture, whereas the embryo is characterized by a feature called self-assembly. Blueprints are “top-down” designs – they don’t assemble themselves into houses. However, embryos do assemble themselves into mature humans. Dawkins goes on to say that self-assembly is achieved through “bottom-up” as opposed to “top-down” architecture: “The beautifully ‘designed’ body emerges as a consequence of rules being locally obeyed by individual cells, with no reference to anything that could be called an overall global plan.” (Dawkins, 2010, p. 220.) Thus there is “no overall plan of development, no blueprint, no architect’s plan, no architect” (2010, p. 247) in the rules governing the development of the embryo.
But if we imagine living things as having been originally designed from the bottom up, then the Darwinian objection to genetic programs being products of Intelligent Design is rendered null and void at one stroke. I have argued above that if living things were originally designed, then they must have been designed in this “bottom-up” fashion.
One scientist who has worked hard to build a link between the biological sciences and information technology is Dr. Don Johnson, author of Programming of Life and Probability’s Nature and Nature’s Probability: A Call to Scientific Integrity. Dr. Johnson has both a Ph.D. in chemistry and a Ph.D. in computer and information sciences. He has spent 20 years teaching in universities in Wisconsin, Minnesota, California, and Europe. On April 8, 2010, Dr. Johnson gave a presentation entitled Bioinformatics: The Information in Life for the University of North Carolina Wilmington chapter of the Association for Computer Machinery. Dr. Johnson’s presentation is now on-line here. Both the talk and accompanying handout notes can be accessed from Dr. Johnson’s Web page. Here’s an excerpt from his presentation blurb:
Each cell of an organism has millions of interacting computers reading and processing digital information using algorithmic digital programs and digital codes to communicate and translate information.
On a slide entitled “Information Systems In Life,” Dr. Johnson points out that:
- the genetic system is a pre-existing operating system;
- the specific genetic program (genome) is an application;
- the native language has a codon-based encryption system;
- the codes are read by enzyme computers with their own operating system;
- each enzyme’s output is to another operating system in a ribosome;
- codes are decrypted and output to tRNA computers;
- each codon-specified amino acid is transported to a protein construction site; and
- in each cell, there are multiple operating systems, multiple programming languages, encoding/decoding hardware and software, specialized communications systems, error detection/correction systems, specialized input/output for organelle control and feedback, and a variety of specialized “devices” to accomplish the tasks of life.
The reason why I have described the programming and code of living things at some length is that there is no known unguided process in the natural world which is capable of generating digital codes, let alone programs. Intelligent Design is the only causally adequate process that can create codes and programs. And if these are an essential feature of cells, then it is reasonable to infer that the first cell was designed.
“Cell or cells?” I hear KeithS ask. “How does all this relate to common descent? And how what does it have to do with the nested taxonomic hierarchy that organisms of every kind belong to?”
In order to answer these questions, I’d like to look at two taxonomic levels: the phylum and the class.
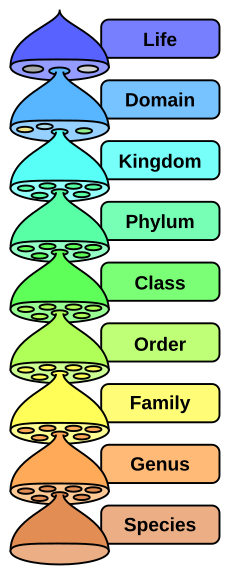 |
The major taxonomic ranks. Image courtesy of Wikipedia.
I’ll start with phyla. The animal kingdom is divided into 40 or so major groups, called phyla; while plants are divided into a dozen or so divisions (which are equivalent to phyla). Other kinds of organisms – including bacteria – have also been classified into phyla. Currently, there is a vigorous and ongoing debate in the scientific community as to whether a phylum should be defined morphologically or phylogenetically. However, a definition of phylum based on an organism’s body plan has recently been championed by paleontologists Graham Budd and Soren Jensen, who are both thorough-going evolutionists. This essentialist account of phyla has the dual advantage of being intellectually elegant and easy to understand, as Professor Michael Behe, a biochemist and noted Intelligent Design proponent, argues in his book, The Edge of Evolution” (2008, Free Press, paperback edition, p. 197):
Animals are divided into a number of groups according to their general “body plan.” For example, one group of animals, chordates (which includes vertebrates like us), have a nerve chord arranged in the back of their bodies, whereas arthropods, the group that includes insects and crustaceans, have a nerve chord in the front. Biologists count dozens of fundamentally different body plans. Types of animals that have the same body plan are generally grouped together in the same phylum, which is the biological classification right under kingdom (kingdom divides organisms into bacteria, plants, animals, and a few other categories).
Since an animal’s body plan is the product of programs operating within the developing embryo (including not only the genetic program but also the epigenetic program), it follows that the taxonomic division of organisms into different phyla reflects the underlying design of the developmental programs that generate these organisms. Each phylum that we find in Nature can thus be regarded as a distinct and well-defined variation of the underlying developmental program.
The next taxonomic level below the level of phylum is that of the class. For instance, cartilaginous fish, bony fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals are classes which belong in the phylum of chordates (Chordates). In his book, The Edge of Evolution, Professor Behe points out that these vertebrate classes differ in the number of distinct cell types they have: “Although amphibians have about 150 cell types and birds about 200, mammals have about 250” (2008, Free Press, paperback edition, p. 199). Each cell type is quite distinct from the other types in its group. For instance, the cells of the mammary, lacrimal and ceruminous glands share the property of being specialized for secretion through ducts (exocrine secretion), but the substances they secrete are very different: milk, tears and ear wax respectively. Professor Behe argues that the gene regulatory network that is required to specify each cell type is irreducibly complex, and he estimates that the number of protein factors involved in the gene regulatory network for each cell type is about ten. There is an old Chinese proverb that a picture is worth a thousand words, and it’s certainly true in this case. Readers who want to see what a gene regulatory network looks like for a tissue type called endomesoderm, in simple sea urchins, can click here. It’s well worth having a look at. The resemblance to a logic circuit is striking, and the impression of design overwhelming.
Behe concludes that the cell types that characterize a class of organisms are very likely to be designed (ibid., pp. 198-199).
Additionally, we may also conclude that if classes are characterized by their own unique cell types, then classes are objective natural categories, with sharply defined boundaries. Moreover, because the different cell types we find in a living organism are all generated by a single gene regulatory network, we can speak of them all as being “variations on the same theme.”
To sum up: we would expect a taxonomic nested hierarchy in organisms which are generated by developmental programs, whose variations at key junctures are what is ultimately responsible for living things falling into different taxa (or categories). If living things are put together in this way, then both the taxonomic hierarchy and the structural hierarchy which are found in living things are features that we would expect life to exhibit.
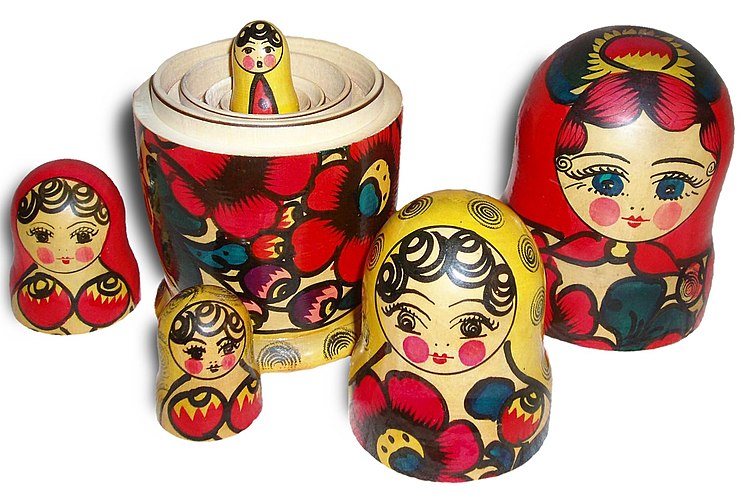 |
Russian matryoshka dolls. Each doll is encompassed inside another until the smallest one is reached. This is the concept of nesting. When the concept is applied to sets, the resulting ordering is a nested hierarchy. Image courtesy of Wikipedia.
Before I address the question of common descent, I’d like to close with a short but relevant excerpt from the Wikipedia article on Hierarchy:
A nested hierarchy or inclusion hierarchy is a hierarchical ordering of nested sets. The concept of nesting is exemplified in Russian matryoshka dolls. Each doll is encompassed by another doll, all the way to the outer doll. The outer doll holds all of the inner dolls, the next outer doll holds all the remaining inner dolls, and so on…
A containment hierarchy is a direct extrapolation of the nested hierarchy concept. All of the ordered sets are still nested, but every set must be “strict” — no two sets can be identical. The shapes example above can be modified to demonstrate this:
Square < Quadrilateral < Polygon < Shape
The notation "x < y" means "x is a subset of y but is not equal to y."
Two types of containment hierarchies are the subsumptive containment hierarchy and the compositional containment hierarchy. A subsumptive hierarchy "subsumes" its children, and a compositional hierarchy is "composed" of its children. A hierarchy can also be both subsumptive and compositional.[10]
A compositional containment hierarchy is an ordering of the parts that make up a system — the system is "composed" of these parts. Most engineered structures, whether natural or artificial, can be broken down in this manner.
The compositional hierarchy that every person encounters at every moment is the hierarchy of life.
I submit that if most engineered structures embody a compositional containment hierarchy, then surely the default expectation for intelligently designed life on Earth is that it would embody such a hierarchy, too.
Evidence for common descent
The reader might be wondering why I continue to accept the evidence for common descent, since I’ve just refuted the most powerful argument in its favor: the existence of a taxonomic nested hierarchy which all organisms can be grouped into. My reply is that it isn’t the evidence from hierarchy theory, DNA similarities, comparative anatomy, or embryology that persuades me of the truth of common descent. The alternative theory (put forward by Richard Owen, among others) that living things were created according to certain archetypes in the Mind of the Designer of Nature could explain these things equally well. I am considerably more impressed by fossil evidence showing, for instance, that the first fully aquatic whales (Basilosaurus and Dorudon) had an intermediate-sized vestigial pelvis and rear limb bones, suggesting that their ancestors lived on land. Although one might reasonably object that the vast majority of fossils don’t show any evidence for common descent, the few that do are very striking: it is remarkable that Archaeopteryx, the oldest universally accepted fossil bird, had twenty bones in its tail, like reptiles, instead of six, as modern birds do. But it is the evidence of atavisms (or “throw-backs”), and anatomical and molecular vestiges in organisms that constitutes, to my mind, the most powerful argument for common descent. Here is how Dr. Theobald presents the argument in his essay, 29+ Evidences for Macroevolution:
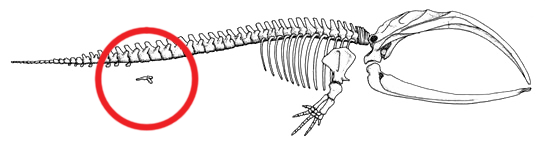 |
Skeleton of a Baleen whale circling the hind limbs and pelvic structure. Some baleen whales actually have visible hindlimbs. Some even have feet with toes on them. Image courtesy of Azcolvin429 and Wikipedia.
Probably the most well known case of atavism is found in the whales. According to the standard phylogenetic tree, whales are known to be the descendants of terrestrial mammals that had hindlimbs. Thus, we expect the possibility that rare mutant whales might occasionally develop atavistic hindlimbs. In fact, there are many cases where whales have been found with rudimentary atavistic hindlimbs in the wild (see Figure 2.2.1; for reviews see Berzin 1972, pp. 65-67 and Hall 1984, pp. 90-93). Hindlimbs have been found in baleen whales (Sleptsov 1939), humpback whales (Andrews 1921) and in many specimens of sperm whales (Abel 1908; Berzin 1972, p. 66; Nemoto 1963; Ogawa and Kamiya 1957; Zembskii and Berzin 1961). Most of these examples are of whales with femurs, tibia, and fibulae; however, some even include feet with complete digits…
A vestige is defined, independently of evolutionary theory, as a
reduced and rudimentary structure compared to the same complex structure in other organisms. Vestigial characters, if functional, perform relatively simple, minor, or inessential functions using structures that were clearly designed for other complex purposes. Though many vestigial organs have no function, complete non-functionality is not a requirement for vestigiality…For example, wings are very complex anatomical structures specifically adapted for powered flight, yet ostriches have flightless wings. The vestigial wings of ostriches may be used for relatively simple functions, such as balance during running and courtship displays — a situation akin to hammering tacks with a computer keyboard. The specific complexity of the ostrich wing indicates a function which it does not perform, and it performs functions incommensurate with its complexity. Ostrich wings are not vestigial because they are useless structures per se, nor are they vestigial simply because they have different functions compared to wings in other birds. Rather, what defines ostrich wings as vestigial is that they are rudimentary wings which are useless as wings.
There are many examples of rudimentary and nonfunctional vestigial characters carried by organisms, and these can very often be explained in terms of evolutionary histories. For example, from independent phylogenetic evidence, snakes are known to be the descendants of four-legged reptiles. Most pythons (which are legless snakes) carry vestigial pelvises hidden beneath their skin (Cohn 2001; Cohn and Tickle 1999). The vestigial pelvis in pythons is not attached to vertebrae (as is the normal case in most vertebrates), and it simply floats in the abdominal cavity. Some lizards carry rudimentary, vestigial legs underneath their skin, undetectable from the outside (Raynaud and Kan 1992).
Snakes may occasionally have vestigial legs or arms, but they should never be found with small, vestigial wings….
Endogenous retroviruses provide yet another example of molecular sequence evidence for universal common descent. Endogenous retroviruses are molecular remnants of a past parasitic viral infection. Occasionally, copies of a retrovirus genome are found in its host’s genome, and these retroviral gene copies are called endogenous retroviral sequences. Retroviruses (like the AIDS virus or HTLV1, which causes a form of leukemia) make a DNA copy of their own viral genome and insert it into their host’s genome. If this happens to a germ line cell (i.e. the sperm or egg cells) the retroviral DNA will be inherited by descendants of the host. Again, this process is rare and fairly random, so finding retrogenes in identical chromosomal positions of two different species indicates common ancestry.
Dr. Theobald goes on to point out that there are at least seven different known instances of common retrogene insertions between chimps and humans.
It has been suggested that target-site preferences account for the shared distributions of endogenous retroviruses, but the main problem with this suggestion (so I have been told by a competent biologist) is that they are nowhere near locus specific enough to do so. Even if they were, one would still need to explain:
(a) the shared orientations of orthologous ERVs;
(b) the nested hierarchical distribution of ERVs within primate genomes (in particular, the distribution of similarities and differences); and
(c) the striking correlation between the distribution of ERV placement and that of point mutations in env, gag, and pol genes.
The biological function of ERVs has little relevance to the argument for common ancestry. Target-site duplication is the hallmark of insertion, regardless of whether the inserts are functional or not. In any case, it is doubtful whether there is a single known case of an entire ERV which is functional. Instead, what scientists typically find is that it is particular ERV components that are functional, rather than the entire sequence.
In brief: there appears to be good circumstantial evidence for the common descent of living organisms, even if we leave aside the evidence of the nested taxonomic hierarchy which the various kinds of organisms can be grouped into, as well as the pervasive genetic, anatomical and embryological similarities between the different kinds of living things.
Is common descent a natural prediction of Intelligent Design Theory?
(i) Why an old earth?
First, I’d like to propose e two fairly obvious reasons why an Intelligent Designer would not have wanted complex animals to appear instantaneously, on the early Earth.
 |
An artist’s conception of how the planet Mars could be terraformed. Four stages of development are depicted. Image courtesy of Daein Ballard and Wikipedia.
(a) Terra-forming. Complex animals have their own specialized physiological needs, to support their uniquely active way of life. Some changes in the Earth’s environment may have been required before complex animals could appear. For instance, recent research suggests that volcanically active mid-ocean ridges caused a massive and sudden surge of the calcium concentration in the oceans, making it possible for marine organisms to build skeletons and hard body parts for the first time. (See Xavier Fernandez-Busquets, Andre Kornig, Iwona Bucior, Max M. Burger, and Dario Anselmetti. Self-Recognition and Ca2+-Dependent Carbohydrate-Carbohydrate Cell Adhesion Provide Clues to the Cambrian Explosion. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2009; 26 (11): 2551.) Geological transformations take time to attain chemical equilibrium. Lest anyone think that this calcium upsurge “explains” the Cambrian explosion: it should be borne in mind that a necessary condition is not the same as a sufficient condition. Calcium upsurges don’t explain how hierarchical patterns of protein regulation suddenly arose in animals from that time.
(b) Ecological engineering. The appearance of complex animals would have added to the complexity of ecosystems. There would have been an increase in the number of needs that the first bilaterian animals had to meet, as complex ecological interactions developed. (See Marshall, C.R. (2006). Explaining the Cambrian “Explosion” of Animals. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Vol. 34: 355-384. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.earth.33.031504.103001. ) It takes time to set up a self-sustaining food chain. Once again: ecological explanations of the Cambrian explosion are well suited to explaining why there had to have been a rapid increase in both disparity and diversity, but by themselves, they cannot explain why the “explosion” happened when it did. Nor can they explain how hierarchical patterns of protein regulation suddenly arose in animals from that time.
(ii) Why common descent?
Next, I’d like to suggest that the Designer’s modus operandi can be described by what might be called an Economy of Effort Principle. Very roughly, it states that out of all the possible sets of mutually compatible intelligent and sentient life-forms that the Designer could have made, the Designer will choose to make that set of intelligent and sentient life-forms which is the easiest for Him to produce, and that He will produce the life-forms belonging to that set in the simplest manner possible, where the terms “easy” and “simple” refer to the total length of the assembly instructions for all species.
The separate creation of each and every kind of creature is one way of generating sentient and sapient life-forms, but because these life-forms share many of their genes, there’s bound to be a lot of duplication in their descriptions. If we accept special creation, then the assembly instructions for each species will have to be specified separately, because each species is created separately. Hence the recipe which provides a complete description of all the actions performed by the Designer in designing all species will be unnecessarily long, thereby violating the Economy of Effort principle.
Many people think that front-loading would be the most economical way for an Intelligent Designer to produce intelligent and sentient life-forms. They argue that the Creator should be able to make a universe that can generate life automatically, without Him needing to “fix” or “adjust” it. But that assumption may be wrong. Recently, physicist Robert Sheldon wrote a thought-provoking article entitled, The Front-Loading Fiction (July 1, 2009), in which he critiqued the assumptions underlying “front-loading.”
In the first place, the clockwork universe of Laplacean determinism (the idea that you can control the outcomes you get, by controlling the laws and the initial conditions) won’t work:
First quantum mechanics, and then chaos-theory has basically destroyed it, since no amount of precision can control the outcome far in the future. (The exponential nature of the precision required to predetermine the outcome exceeds the information storage of the medium.) (Emphasis mine – VJT.)
As far as I know, no-one in the “theistic evolution” camp has addressed this basic point raised by Dr. Sheldon. Even today, one still commonly hears objections to Intelligent Design like the following: “Wouldn’t it be more elegant of God to design a universe in which the laws of Nature would generate life automatically?” as if that were a genuine possibility.
In the second place, what Dr. Sheldon calls “Turing-determinism” – the modern notion that God could use an algorithm or program to design all the forms we observe in Nature – fares no better:
Turing-determinism is incapable of describing biological evolution, for at least three reasons: Turing’s proof of the indeterminacy of feedback; the inability to keep data and code separate as required for Turing-determinacy; and the inexplicable existence of biological fractals within a Turing-determined system.
Specifically, Dr. Sheldon argues that the only kind of universe that could be pre-programmed to produce specific results without fail and without the need for further input would be a very boring, sterile one, without any kind of feedback, real-world contingency or fractals. However, such a universe would necessarily be devoid of any kind of organic life. Dr. Sheldon proposes that God is indeed a “God of the gaps” – an incessantly active “hands-on” Deity Who continually maintains the universe at every possible scale of time and space, in order that it can support life. Such a role, far from diminishing God, actually enhances His Agency.
The conclusion we have reached, then, is that the common descent of living organisms is a reasonable (if not compelling) prediction, from an Intelligent Design perspective. Front-loading probably won’t do the trick: it seems that there is still too much “hands-on” work that a Designer would need to do, to generate complex sentient and sapient life-forms.
Creation or evolution? It depends on how you look at it
But the fascinating conclusion that the latest research is pointing to is that from a formal perspective, each species of living thing can be viewed as a creation in its own right, notwithstanding its common ancestry with other species at a material level.
In a recent post, The Edge of Evolution?, I drew readers’ attention to a 2011 paper by the Croatian biochemist Dr. Branko Kozulic, titled, Proteins and Genes, Singletons and Species, which argues that the presence of not one but literally hundreds of chemically unique proteins in each species is an event beyond the reach of chance, and that since these proteins exhibit specified complexity (as the amino acids which make up the polypeptide chain need to be in the correct order), each species must therefore be the result of intelligent planning. (A parallel argument can be made for de novo protein-coding genes.) I also discussed some possible implications of Dr. Kozulic’s research in a follow-up post titled, Some testable predictions entailed by Dr. Kozulic’s model of Intelligent Design.
What the new research suggests is that regardless of whether species are linked by a common family tree or not, a lot of engineering must have gone into the design of each and every species. Literally hundreds of chemically unique proteins and genes must have been designed for each and every kind of living thing on Earth, genetic and anatomical similarities notwithstanding. All of this renders the 150-year-old dispute over creation vs. common descent rather moot. The singular fact that needs to be explained is the evidence of careful planning that we see in the design of living things.
The wrong map?
In his article, KeithS likens Intelligent design proponents to people wandering around with inaccurate maps of the world, leading them to falsely claim that some paths cannot be traversed when in fact they can. In response, I would argue that the truth is the other way round. It is the Darwinists who have the wrong map.
The Intelligent Design argument I’ll be putting forward here is a very simple one. In a nutshell, my argument is all about proteins. Proteins perform very specific functions within the cell. What’s more, living things need lots of proteins: the simplest living cell needs at least 250 proteins; the molecular machines within the cell require dozens of proteins each; the first eukaryotic cell (i.e. a cell having a nucleus, as cells in animals, plants, fungi and protists do) requires hundreds more proteins than a simple bacterial cell; and the new cell types which appeared in the bodies of complex animals required layers upon layers of protein regulation, in a hierarchical system of control. However, as far as we can tell, the odds of even a single protein forming by blind processes (chance plus necessity) are astronomically low: well below 1 in 10 to the power of 150. That’s so rare that you wouldn’t expect it to happen even once, in the lifetime of the observable universe. Short of positing a supernatural act, the only way to narrow those odds is to suppose that either the starting conditions of the universe were rigged, or the laws of Nature are somehow rigged in ways unknown to us, so as to favor the evolution of proteins. But it takes an intelligent being to rig things like that, so we’re back with a Designer.
My Intelligent Design argument can be formulated on six levels, as there are at least six kinds of functional specificity in living things that point to their having been intelligently designed:
(1) Proteins. Every living thing on this planet contains proteins, which are made up of amino acids. Proteins are fundamental components of all living cells and include many substances, such as enzymes, hormones, and antibodies, that are necessary for the proper functioning of an organism. They’re involved in practically all biological processes. To fulfil their tasks, proteins need to be folded into a complicated three-dimensional structure. Proteins can tolerate slight changes in their amino acid sequences, but a single change of the wrong kind can render them incapable of folding up, and hence, totally incapable of doing any kind of useful work within the cell. That’s why not every amino-acid sequence represents a protein: only one that can fold up properly and perform a useful function within the cell can be called a protein. Now let’s consider a protein made up of 150 amino acids – which is a fairly modest length. If we compare the number of 150-amino-acid sequences that correspond to some sort of functional protein to the total number of possible 150-amino-acid sequences, we find that only a tiny proportion of possible amino acid sequences are capable of performing a function of any kind. The vast majority of amino-acid sequences are good for nothing. So, what proportion are we talking about here? An astronomically low proportion: 1 in 10 to the power of 74, according to work done by Dr. Douglas Axe. When we add the requirement that a protein has to be made up of amino acids that are either all left-handed or all right-handed, and when we finally add the requirement that the amino acids have to be held together by peptide bonds, we find that only 1 in 10 to the power of 164 amino-acid sequences of that length are suitable proteins. 1 in 10 to the power of 164 is 1 in 1 followed by 164 zeroes. The Earth has been around for 4,500,000,000 years, but it should be obvious to the reader that that’s nowhere near enough time for a protein to form as a result of unguided natural processes. To get round this difficulty, scientists have hypothesized that maybe Nature has a hidden bias that makes proteins more likely to form, but all the evidence suggests there isn’t any such bias – and even if there were one, that would need explaining too. Finally, scientists have suggested that maybe another molecule – RNA – formed first, and proteins came later, but the same problem arises for RNA: the vast majority of possible sequences are non-functional, and only an astronomically tiny proportion work.
(2) The simplest living cell. Even a minimally complex cell needs at least 250 proteins, for it to work. If the odds of generating even one protein by blind processes during the 4.5-billion-year history of the Earth are astronomically low, then the odds of generating a living cell are much, much worse. To get round this difficulty, some scientists have hypothesized that the first living things didn’t contain proteins: they used RNA instead. But as we saw above, the same problem arises for RNA: only an astronomically tiny proportion of possible sequences can do any useful work, so the chances of a useful RNA molecule forming are very, very low. To get round these astronomical odds, other scientists have proposed that the first living things were made up of something shorter: polypeptides, or TNA. But polypeptides and TNA aren’t alive: even if they could replicate, they can’t evolve. What’s more, all the living things we know of contain very long digital code sequences. For instance, the DNA letters of the genome of the simplest free-living organism – Mycoplasma genitalium – would span 147 pages, if they were printed in 10 point font. So the hypothesis that the first living things were much shorter than they were today is unsupported by any evidence. Finally, some scientists have proposed that the first living things were made of something more exotic than DNA or RNA – maybe clay crystals. But once again, that’s pure supposition, which isn’t backed up by any hard evidence.
(3) Molecular machines. Most cellular functions are executed by complexes containing multiple proteins. These proteins work together in sync, acting like molecular machines. A molecular machine is an assemblage of parts that transmit energy from one to another in a predetermined manner. In living things – even the simplest ones – these machines are each composed of dozens or even hundreds of protein components. If the odds of generating even one functional protein by blind processes are astronomically low, the odds of making a molecular machine are unimaginably low. Some scientists have argued that these molecular machines may have once been simpler, on the grounds that some of the proteins in these machines appear to have been derived from other ones. That’s true, but even when you take out the derived proteins that came along later, you’re still stuck with machines that have dozens or even hundreds of components. So the problem remains.
(4) Eukaryotic cells. Plants, animals, fungi, slime moulds, protozoa and algae are all made up of eukaryotic cells. A eukaryotic cell is like a miniature factory. The cell nucleus contains a multitude of robot-like machines working in synchrony, which shuttle a huge range of products and raw materials along conduits leading to and from the various assembly plants in the outer parts of the cell. Everything is precisely choreographed. A eukaryotic cell exhibits features such as quality control, feedback systems and automated parcel processing (“zip codes”). What’s more, each cell has to be capable of replicating its entire structure within just a few hours. To do all these things, a eukaryotic cell requires thousands of different kinds of proteins. Some scientists have proposed that eukaryotic cells formed gradually in a step-by-step process called endosymbiosis, where one smaller organism came to live inside another, and it’s true that some parts of the eukaryotic cell, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts, seem to have arisen that way. But that doesn’t explain the origin of the nucleus of the cell, which is where most of the DNA resides. A nucleus requires hundreds of different kinds of proteins for it to do its work: an evolutionist’s nightmare.
(5) Animals with complex body plans (e.g. arthropods, annelid worms, molluscs, echinoderms and chordates, as opposed to simple animals like sponges and coelenterates). Complex animals need more cell types in order to perform their diverse functions. New cell types require many new and specialized proteins. But these new proteins also have to be organized into new, hierarchically ordered systems within the cell. That’s because in complex animals, new cell types need to be organized into new tissues, organs, and body parts, which in turn have to be organized to form body plans. In other words, complex animals embody hierarchically organized systems of lower-level parts within a functional whole. So we’re not only talking about lots of proteins, we’re talking about proteins organized into hierarchical levels of control. Once again, no evolutionist has put forward a quantifiable model of how these levels of control might have arisen.
(6) Species. As we have seen, each species of living thing turns out to have literally hundreds of chemically unique proteins. Once again, this is a specified event beyond the reach of chance, forcing us to conclude that each and every species must have been designed.
The evidence for Intelligent Design stems from an attribute of life which is even more fundamental than the taxonomic hierarchy that organisms belong to – namely, the high degree of functional specified complexity we find in living things. It is this singular fact which Darwinists have shown themselves utterly unable to account for, and which leads me to conclude that Darwinism is a failure as an explanation of life, in all its glorious diversity.