Darwinism from an informatics point of view
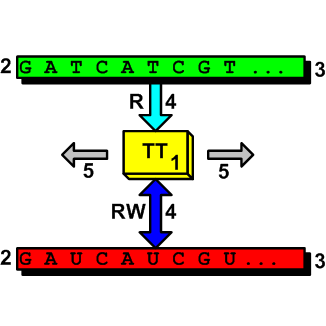
 As everyone knows, life in all its countless instances (organisms) involves internal instructions, as well as processors that run them. Without these instructions, no organism would be able to originate in the first place, let alone develop or survive. The discovery of these instructions – contained in DNA/RNA macromolecules and the molecular machinery that reads and writes them in biological cells – has been hailed as one of the greatest theoretical and experimental breakthroughs of the 20th century. The ID movement claims that these scientific findings have only served to highlight the weaknesses and inconsistencies of the neo-Darwinian theory of macro-evolution, according to which all species have evolved from a common ancestor, as a result of random mutation and natural selection. Read More ›
As everyone knows, life in all its countless instances (organisms) involves internal instructions, as well as processors that run them. Without these instructions, no organism would be able to originate in the first place, let alone develop or survive. The discovery of these instructions – contained in DNA/RNA macromolecules and the molecular machinery that reads and writes them in biological cells – has been hailed as one of the greatest theoretical and experimental breakthroughs of the 20th century. The ID movement claims that these scientific findings have only served to highlight the weaknesses and inconsistencies of the neo-Darwinian theory of macro-evolution, according to which all species have evolved from a common ancestor, as a result of random mutation and natural selection. Read More ›