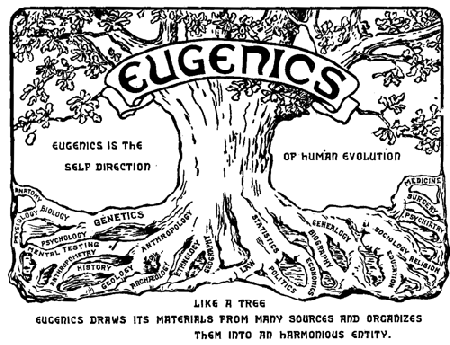
Notoriously, the Second International Congress on Eugenics [1921] defined Eugenics as the self-direction of human evolution and saw eugenics as applied evolutionary science with intellectual, logical and factual roots in several linked branches of science, medicine and scholarship.
If you doubt this, simply examine the logo to the right.
Perhaps the best summary of the then prevailing mentality comes from Scientific Monthly, in an article on the congress — noting how it highlights a keynote by a son of Darwin:
>>THE SECOND INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF EUGENICS
In this journal special attention has always been given to problems of evolution, heredity and eugenics. As older readers of the THE POPULAR SCIENCE MONTHLY will remember, it gave the first American publication to the work of Spencer, and, to a certain extent of Darwin, Huxley and the other leaders in the develop- ment of the doctrine of evolution. It was indeed under the elder You- mans a journal primarily devoted to the cause of evolution at a time when the word stood for heresy not only with the general public, but also among most men of science.
During the past twenty years under its present editorial control, THE SCI- ENTIFIC MONTHLY has continued to devote a considerable part of its space to work bearing on heredity and eugenics. Francis Galton printed here articles laying the foundation of eugenics, and the leading American students of genetics-Brooks, Wilson, Morgan, Conklin, Davenport, Jen- nings, Pearl and many others have communicated the results of their work to the wider scientific and edu- cated public through this journal. In like manner, many articles by leaders in the subject have been printed on human heredity in so far as it is open to experimental or statistical study, and in other subjects on which a sci- ence of eugenics must rest-popula- tion, birth and death rates, immigra- tion, racial differences, human be- havior, etc.
We are consequently pleased to be able to record the holding in New York City of the second International Congress of Eugenics and to print in the present issue of the MONTHLY several of the more important ad- dresses by foreign representatives.
Shakespeare left no descendants, and Ben Jonson remarked that nature, having made her masterpiece, broke the mold. The four sons of Charles Darwin have followed scientific ca- reers, a fine example of family heredity and tradition. It is a special privilege to welcome to the United States and to print the address in advocacy of eugenics of Major Leon- ard Darwin, based so largely on the works of his father, Charles Dar- win, and of his cousin, Francis Galton. We hope to be able to publish in subsequent issues a gen- eral account of the congress by Dr. C. C. Little, the secretary, and several of the papers containing the results of more special scientific research.
The program was strong in genetics, in which America now. probably is leading. But all the divisions main- tained good standards, the more doubtful theories and premature ap- plications of ignorance, to which newer sciences such as eugenics and psychology are subject, having been in general avoided.>>
The Canadian Eugenics Archive adds:
>>The Congress was made up of four section[s], the first was “Human and Comparative Heredity,” the second was “Eugenics and the Family”, the third was “Human Racial Differences,” and the fourth was “Eugenics and the State” (International Eugenics Congress, 1934). An Exhibition was also prepared for the public at large, include those without academic training (International Eugenics Congress, 1934). The goal of the Congress was to discuss eugenics, but particularly in a climate of international cooperation for eugenics goals (International Eugenics Congress, 1934).
Over 300 people attended the conference. It was generally considered a success, and a committee was formed after the Congress to help educate and promote eugenic ideas in America. This committee eventually became the American Eugenics Society.
The logo of the conference was a tree – an enduring symbol of the eugenics movement.>>
Such, should already establish how the relevant thinking was, by general consent of the guild of scientific scholarship and that of the wider “educated public”
— [e.g. honorary Conference President was Alexander Graham Bell, inventor of telephony and tied to the Grosvenor family which for years dominated National Geographic, which is similar in current impact to the above cited], —
a matter of science rooted in the work of Darwin and Galton. That was the “scientific consensus” of the day; itself a lesson on the intellectual and moral hazards of appeal to consensus in science. Also, we must note the significance of influential media and campaigns by editors embarking on crusades in the building of such a consensus. At that time, G K Chesterton was very much an outlier, a lone voice pointing out the errors and hazards.
It is the consequences over the next twenty-five years and the general horror that resulted, which led to a change of approach.
In this light, let us now view some of Darwin’s key remarks in his second book, Descent of Man:
>[CH 5:] The lower animals, . . . must have their bodily structure modified in order to survive under greatly changed conditions. They must be rendered stronger, or acquire more effective teeth or claws, for defence against new enemies; or they must be reduced in size, so as to escape detection and danger. When they migrate into a colder climate, they must become clothed with thicker fur, or have their constitutions altered. If they fail to be thus modified, they will cease to exist.
The case, however, is widely different, as Mr. Wallace has with justice insisted, in relation to the intellectual and moral faculties of man. These faculties are variable; and we have every reason to believe that the variations tend to be inherited. [–> notice, the key issue of superior/inferior descent among human populations] Therefore, if they were formerly of high importance to primeval man and to his ape-like progenitors, they would have been perfected or advanced through natural selection. [–> notice, natural selection] Of the high importance of the intellectual faculties there can be no doubt, for man mainly owes to them his predominant position in the world.
We can see, that in the rudest state of society, the individuals who were the most sagacious, who invented and used the best weapons or traps, and who were best able to defend themselves, would rear the greatest number of offspring. The tribes, which included the largest number of men thus endowed, would increase in number and supplant other tribes. [–> as in, eliminate and/or replace] Numbers depend primarily on the means of subsistence, and this depends partly on the physical nature of the country, but in a much higher degree on the arts which are there practised. As a tribe increases and is victorious, it is often still further increased by the absorption of other tribes.* The stature and strength of the men of a tribe are likewise of some importance for its success, and these depend in part on the nature and amount of the food which can be obtained.
In Europe the men of the Bronze period were supplanted by a race more powerful, and, judging from their sword-handles, with larger hands;*(2) but their success was probably still more due to their superiority in the arts.>>
That already demonstrates the basic point. But in Ch 6, we find much more:
>>[CH 6:] EVEN if it be granted that the difference between man and his nearest allies is as great in corporeal structure as some naturalists maintain, and although we must grant that the difference between them is immense in mental power, yet the facts given in the earlier chapters appear to declare, in the plainest manner, that man is descended from some lower form, notwithstanding that connecting-links have not hitherto been discovered. Man is liable to numerous, slight, and diversified variations, which are induced by the same general causes, are governed and transmitted in accordance with the same general laws, as in the lower animals.
Man has multiplied so rapidly, that he has necessarily been exposed to struggle for existence [–> key phrase], and consequently to natural selection. [–> again] He has given rise to many races, some of which differ so much from each other, that they have often been ranked by naturalists as distinct species. [–> key racist principle, here, cf. the sub-title of Origin, about preservation of favoured races in the struggle for survival] His body is constructed on the same homological plan as that of other mammals. He passes through the same phases of embryological development. He retains many rudimentary and useless structures, which no doubt were once serviceable. Characters occasionally make their re-appearance in him, which we have reason to believe were possessed by his early progenitors. If the origin of man had been wholly different from that of all other animals, these various appearances would be mere empty deceptions; but such an admission is incredible. [–> notice, yet another theological appeal by Darwin] These appearances, on the other hand, are intelligible, at least to a large extent, if man is the co-descendant with other mammals of some unknown and lower form . . . .
The great break in the organic chain between man and his nearest allies, which cannot be bridged over by any extinct or living species, has often been advanced as a grave objection to the belief that man is descended from some lower form [–> notice, the fossil gaps question]; but this objection will not appear of much weight to those who, from general reasons, believe in the general principle of evolution.
[–> a double-edged sword, this: at what point does cumulative systematic evidence of gaps begin to count? for many, patently, never]
Breaks often occur in all parts of the series, some being wide, sharp and defined, others less so in various degrees; as between the orang and its nearest allies- between the Tarsius and the other Lemuridae- between the elephant, and in a more striking manner between the Ornithorhynchus or Echidna, and all other mammals. But these breaks depend merely on the number of related forms which have become extinct.
At some future period, not very distant as measured by centuries, the civilised races of man will almost certainly exterminate, and replace, the savage races throughout the world. At the same time the anthropomorphous apes, as Professor Schaaffhausen has remarked,* [ * Anthropological Review, April, 1867, p. 236] will no doubt be exterminated. The break between man and his nearest allies will then be wider, for it will intervene between man in a more civilised state, as we may hope, even than the Caucasian, and some ape as low as a baboon, instead of as now between the negro or Australian and the gorilla. With respect to the absence of fossil remains, serving to connect man with his ape-like progenitors, no one will lay much stress on this fact who reads Sir C. Lyell’s discussion,* where he shews that in all the vertebrate classes the discovery of fossil remains has been a very slow and fortuitous process. Nor should it be forgotten that those regions which are the most likely to afford remains connecting man with some extinct ape-like creature, have not as yet been searched by geologists. [–> the familiar argument, now 140+ years old . . . 1/4 million fossil species, millions of exemplars in museums etc, billions more seen in the ground] >>
It is clear from these writings, that the science is deeply connected to what would be elaborated as eugenics etc. We need to frankly face that, acknowledge it and learn from it if we are to make genuine onward progress. END